All keys adapted from Anderson & Allen, 2001.1
-
- Spinous portion of dorsal fin deeply incised at its junction with soft portion; dorsal fin with 10 spines and 11 (rarely 10) soft rays Etelis species
- Spinous portion of dorsal fin not deeply incised at its junction with soft portion; dorsal fin with 10 spines and 10 soft rays Paracaesio species
-
- Premaxillae essentially not protrusible, attached to snout at symphysis by a frenum Aphareus species
- Premaxillae protrusible, not attached to snout by frenum 5
-
- Groove present on snout below nostrils; pectoral fins less than ½ length of head Aprion virescens
- No groove on snout; pectoral fins a little shorter than head to somewhat longer than head Pristipomoides species
-
- Upper lip with a median fleshy protrusion, well developed in adults; spines of dorsal and anal fins strong, very robust in large adults Lipocheilus carnolabrum
- Upper lip without a median fleshy protrusion Paracaesio species
-
- Anterior profile quite steep; dorsal fin with 10 spines and 17–19 soft rays; upper and lower pharyngeals enlarged and bearing large molariform teeth Symphorichthys spilurus
- Anterior profile sloping more gently; dorsal fin with 10 spines and 14–17 soft rays; upper and lower pharyngeals not particularly enlarged, not bearing molariform teeth Symphorus nematophorus
-
- First gill arch with 60 or more gill rakers on lower limb Macolor species
- First gill arch with 20 or fewer gill rakers on lower limb 11
-
- Upper and lower profiles of head equally rounded; eye set toward middle of head; mouth rather small, somewhat upturned; no fang-like canines at anterior ends of jaws Pinjalo species
- Upper and lower profiles of head not equally rounded, upper profile evenly rounded to steeply sloped, and lower profile flattened; eye closer to upper profile of head than to lower; mouth larger, usually not upturned; some fang-like canines usually present at anterior ends of jaws Lutjanus species
-
- First gill arch with 6–12 gill rakers on upper limb and 15–18 on lower limb (total 22–28 including rudiments, if present); body steel blue to purplish brown Aphareus furca
- First gill arch with 16–19 gill rakers on upper limb and 32–35 on lower limb (total 49–52 including rudiments, if present); body blue-grey to reddish Aphareus rutilans
-
- Opercular spine blunt and indistinct, usually covered in skin, tip of upper caudal-fin lobe black Etelis boweni
- Opercular spine pointed and distinct, no black marking on tip of upper caudal-fin lobe Etelis carbunculus
-
- Total gill rakers on first gill arch 32–36, including rudiments; upper lobe of caudal fin slightly longer (30–34% of SL in specimens >130 mm SL) Etelis radiosus
- Total gill rakers on first gill arch 23–28, including rudiments; upper lobe of caudal fin very long (33–75% SL) Etelis coruscans
-
- Preorbital (suborbital) space (distance between upper jaw and eye) very narrow, 9.2–16.3 times in head length; body slender, usually 3 or more times in standard length; soft dorsal-fin rays 12 2
- Preorbital (suborbital) space (distance between upper jaw and eye) wider, 3.3–8.9 times in head length; body deeper, 2.1–3.1 times (but usually <3 times) in standard length; soft dorsal-fin rays usually 13 more (occasionally 12) 3
-
- A dark lateral band from snout to caudal-fin base and 2 pearly white spots above lateral line (1 below spinous portion and other below soft portion of dorsal fin); body depth 3.5–3.8 times in SL; tongue usually smooth, without teeth Lutjanus biguttatus
- Silvery white with a broad yellow lateral stripe and narrow yellowish lines corresponding with longitudinal scale rows; body depth 2.9–3.3 times in SL; tongue with a patch of fine granular teeth Lutjanus lutjanus
-
- Dorsal-fin spines 11 or 12 Lutjanus bengalensis
- Dorsal-fin spines 10 5
-
- Four stripes on sides; belly usually abruptly whitish, often with thin grey lines; scale rows on cheek 5 or 6; upper pectoral-fin rays darkish Lutjanus kasmira
- Five stripes on sides; belly not abruptly whitish and without thin lines; scale rows on cheek 10 or 11; upper pectoral-fin rays pale Lutjanus quinquelineatus
-
- Vomer without teeth; dorsal fin with 10 spines and 14–19 soft rays; 1 or more anterior soft dorsal-fin rays produced as filaments (at least in juveniles) Lutjanus carponotatus
- Vomer with teeth; dorsal fin with 10–12 spines and 11–16 soft rays; none of anterior soft dorsal-fin rays produced as filaments 9
-
- A large black spot usually present on upper sides, juveniles sometimes with an ocellated spot and/or series of 4–7 broad dark stripes on side (adults of L. fulviflamma with yellow stripes) 9
- No black spot present on sides; a series of narrow, yellowish longitudinal lines on side, those on upper back slanting upward toward dorsal-fin base, sometimes an enlarged darker stripe from eye to middle of caudal-fin 10
-
- Soft dorsal-fin rays usually 14; a relatively wide gap between temporal scale bands on each side; black spot on upper side located mainly above lateral line; juveniles with a series of 4–7 broad stripes (blackish to orange or yellow-brown in life) on sides Lutjanus russellii
- Soft dorsal-fin rays usually 13; little or no gap between temporal scale bands on each side; black spot on upper side located mostly below lateral line or bisected by it, sometimes very elongate; juveniles without a series of broad stripes on sides Lutjanus fulviflamma
-
- Midlateral stripe usually broader and darker than other stripes on sides; transverse scale rows on cheek 7–10 Lutjanus vitta
- Midlateral stripe not broader or darker than other stripes on sides; transverse scale rows on cheek usually 6 or 7 (occasionally 8) 11
-
- Predorsal scales extending to mid-interorbital level; a blunt, flattened spine on upper margin of opercle, above the main centrally located spine; interorbital width 4.4–6.5 times in head length; total gill rakers on first gill arch (including rudiments) 18–21 Lutjanus xanthopinnis
- Predorsal scales extending to level of rear part of orbit; no blunt spine on upper margin of opercle; interorbital width 6.5–6.9 times in head length; total gill rakers on first gill arch (including rudiments) 15 or 16 Lutjanus mizenkoi
-
- Total gill rakers on first gill arch 25–30 (including rudiments); caudal fin distinctly forked with rounded lobes Lutjanus gibbus
- Total gill rakers on first gill arch 14–23 (including rudiments); caudal fin emarginate, without rounded lobes 13
-
- Soft anal-fin rays 10; dorsal fin with 11 spines and 16 (rarely 15) rays; colour pattern of 3 dark brown to red transverse bars (sometimes indistinct in large adults) Lutjanus sebae
- Soft anal-fin rays 8 or 9; dorsal fin elements variable, with 10 or 11 spines and 12–16 soft rays; colour not as above 14
-
- Soft dorsal-fin rays 15 or 16; body relatively deep, 2.1–2.4 times in SL; head usually with numerous wavy bluish lines; a white spot often present below junction of spinous and soft parts of dorsal fin (bordered with black in juveniles); lips thick in large adults Lutjanus rivulatus
- Soft dorsal fin rays 13 or 14; body usually more slender, 2.3–2.8 times in SL; colour not as above; lips not thick in adults 16
-
- Caudal fin and outer third of dorsal fin blackish or dusky brown with a narrow white margin Lutjanus fulvus
- Caudal fin yellow or grey basally and yellow distally without narrow white margin; outer third of dorsal fin not distinctly darker than remainder of fin 17
-
- Dorsal-fin spines 10; no yellow stripes on body Lutjanus boutton
- Dorsal-fin spines 11; 10–12 faint yellow stripes on sides Lutjanus rufolineatus
-
- Colour pattern of 8 broad transverse bands or saddles on upper half of body and large black blotch in centre of caudal peduncle Lutjanus semicinctus
- Colour pattern consisting of 5 dark stripes on whitish ground colour; 2 or 3 uppermost stripes crossed by dark vertical bars forming a network of light and dark squares; a larger dark spot at base of caudal fin Lutjanus decussatus
-
-
- Nostrils set in a prominent groove running forward of eye in specimens >200 mm SL; colour generally dark brown on upper back grading to tan or light brownish ventrally; dorsal and caudal fins dusky; outer portions of anal and pelvic fins blackish; juveniles <200 mm TL with usually with 2 whitish spots on upper back Lutjanus bohar
- Nostrils not set in groove at any size; colour pattern not as above 21
-
- Caudal fin with a distinctive crescentic black marking, remainder of body and fins uniformly yellowish with a silvery sheen on lower sides Lutjanus lunulatus
- Caudal fin without a distinctive black marking; colour of body and fins variable 22
-
- A black spot on upper side at level of lateral line below soft dorsal fin (faint or absent in large adults); remainder of body and fins mainly pale; tongue with a patch of fine granular teeth (sometimes absent in juveniles) Lutjanus monostigma
- Black spot on upper side of body absent, although a saddle or spot sometimes present on upper portion of caudal peduncle; tongue smooth 23
-
- Dorsal-fin spines 12; a series of 5 or 6 dusky yellow stripes on sides; longitudinal rows of scales below lateral line rising obliquely Lutjanus dodecacanthoides
- Dorsal-fin spines 10 or 11; colour not as above; longitudinal rows of scales below lateral line parallel to axis of body or rising obliquely 24
-
- Axil of pectoral fins black; colour overall deep red; posterior dorsal-fin and anal-fin rays elongated to form pointed fins; soft anal-fin rays 8 Lutjanus timoriensis
- Axil of pectoral fins without a black marking; colour variable, but often red; posterior dorsal-fin and anal-fin rays low and rounded or tall and pointed, but if tall and pointed specimens usually with 9 soft anal-fin rays 25
-
- Dorsal-fin spines 10; soft anal-fin rays usually 8 (rarely 9); tongue with a patch of fine granular teeth; colour variable, pink to greyish brown; juveniles without a black saddle on upper caudal peduncle 26
- Dorsal-fin spines 11 (rarely 10); soft anal-fin rays usually 9 (occasionally 8); tongue smooth; colour largely reddish; juveniles usually with a black saddle on upper caudal peduncle 28
-
- Interorbital width 4.9–5.2 times in head length; body relatively deep, 2.3–2.5 times in SL; snout-forehead profile flat or slightly convex Lutjanus bitaeniatus
- Interorbital width 5.5–7.6 times in head length; body relatively deep, 2.4–2.8 times in SL; snout-forehead profile slightly concave 27
-
- Lower body and pelvic and anal fins yellow; pectoral-fin rays 17 Lutjanus papuensis
- Body and fins not yellow; pectoral-fin rays 16 Lutjanus lemniscatus
-
- Mouth relatively small, maxilla length much less than distance between bases of last dorsal- and anal-fin rays; interorbital width 3.5–4.8 times in head length (in specimens >150 mm SL); some longitudinal scale rows below lateral line slanting obliquely in posterior direction towards dorsal profile; head profile convex (in specimens >150 mm SL) Lutjanus erythropterus
- Mouth larger, maxilla length about equal to distance between bases of last dorsal- and anal-fin rays; interorbital width 5.1–6.6 times in head length (in specimens >120 mm SL); some longitudinal scale rows below lateral line horizontal (although some rows may slant obliquely in juveniles <100 mm SL); head profile straight or slightly concave Lutjanus malabaricus
-
- Colour pattern consisting of 4 relatively wide dusky brown or blackish stripes on pale ground colour (only known from juveniles <15 cm SL) Lutjanus maxweberi
- Colour pattern not as above 30
-
- Vomerine tooth patch triangular with medial posterior extension; preorbital space narrow, 8.6–10.3 times in head length; a prominent black spot bisected by lateral line below spinous dorsal fin Lutjanus ehrenbergii
- Vomerine tooth patch crescentic to triangular without a medial posterior extension; preorbital space wider, 4.7–4.9 times in head length; black spot on back present or absent 31
-
- A large black spot on upper back usually present; colour pale with each scale on side with a brownish spot forming longitudinal rows Lutjanus johnii
- Black spot on upper back absent, colour dark Lutjanus argentimaculatus
-
- First gill arch (including rudiments) with 37–42 gill rakers on upper limb and 71–81 on lower limb (total 110–122); anal fin with 3 spines and usually 10 (occasionally 11) soft rays; pelvic fins very long and pointed in young, but short and rounded in adults Macolor macularis
- First gill arch (including rudiments) with 26–38 gill rakers on upper limb and 60–71 on lower limb (total 89–107); anal fin with 3 spines and usually 11 (occasionally 10) soft rays; pelvic fins short and rounded at all sizes Macolor niger
-
- Teeth very small, without enlarged canines Paracaesio brevidentata
- Teeth larger, with enlarged canines 3
-
- Body colour dark grey, dark purplish brown or bluish; preopercle with 1 to 3 rows of scales peripheral to and usually distinctly separated from main group of cheek scales Paracaesio sordida
- Caudal fin, upper part of caudal peduncle, and upper side of body to anterior end of dorsal fin yellow; remainder of body mostly blue; preopercle almost always without scales peripheral to main group of cheek scales Paracaesio xanthura
-
- Upper sides with 4 brownish bars; maxilla scaled Paracaesio kusakarii
- Upper sides uniform blue, without vertical bars; maxilla without scales Paracaesio caerulea
-
- Dorsal fin with 11 spines and 14 or 15 soft rays; anal fin with 3 spines and 9 or (usually) 10 soft rays; longest anal-fin spine 2.1–2.65 times in head length; pectoral-fin length 3.05–3.9 times in standard length; pelvic-fin length 1.4–1.65 times in head length; caudal fin deeply emarginate, caudal concavity 2.1–3.6 times in head length; diagonal dark lines following scale rows on nape and upper half to two-thirds of body Pinjalo pinjalo
- Dorsal fin with 12 spines and 13 soft rays; anal fin with 3 spines and 8 or 9 soft rays; longest anal-fin spine 2.7–3.2 times in head length; pectoral-fin length 2.5–3.05 times in standard length; pelvic-fin length 1.65–1.8 times in head length; caudal fin slightly emarginate, caudal concavity 3.55–5.45 times in head length; no diagonal dark lines on nape and body Pinjalo lewisi
-
- Two golden stripes bordered with blue on snout and cheek; transverse vermiculations on top of head; suborbital wide, its width 7 times in head length at 15 cm standard length, 5.5 times at 25 cm, 4 times at 40 cm Pristipomoides multidens
- No golden stripes on snout and cheek; longitudinal vermiculations on top of head; suborbital narrow, its width 8.4 times in head length at 15 cm standard length, 7.3 times at 25 cm, 5.8 times at 40 cm Pristipomoides typus
-
- Vomerine tooth patch with medial posterior extension (vomerine tooth patch sometimes diamond-shaped); patch of teeth on tongue Pristipomoides sieboldii
- Vomerine tooth patch triangular in shape, without medial posterior extension; no teeth on tongue Pristipomoides auricilla
-
- Sides with alternating oblique red and yellow bars; lateral-line scales (tubed) 63–67 Pristipomoides zonatus
- Sides without red and yellow bars; lateral-line scales (tubed) 57–63 6
-
- Sides with numerous irregular dark markings, including zigzag line that runs at about level of lateral line anteriorly and then onto dorsolateral part of caudal peduncle posteriorly; total gill rakers (including rudiments) on first gill arch 17–21; depth of body 2.8–3.1 times in SL Pristipomoides argyrogrammicus
- Sides without irregular dark markings; total gill rakers (including rudiments) on first gill arch 22–27; depth of body 3–3.8 times in SL 7
-
- Length of upper jaw 2.4–2.7 times in head length; caniniform teeth at anterior ends of jaws not appreciably enlarged Pristipomoides filamentosus
- Length of upper jaw 2.1–2.4 times in head length; canine teeth at anterior ends of both jaws usually enlarged Pristipomoides flavipinnis
Caesionidae
Fusiliers
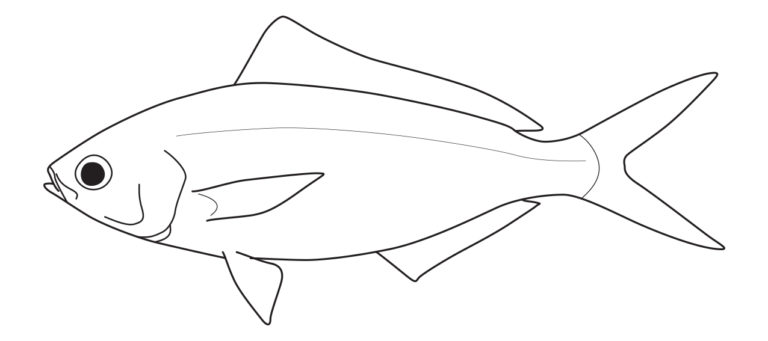
Caesionidae differ in having a mouth small (vs. fairly large); premaxillae extremely protrusible (vs. premaxillae moderately protrusible or fixed); teeth in jaws small or minute (vs. usually distinct); premaxilla, vomer, and palatine teeth usually absent (vs. premaxilla, vomer, and palatine teeth typically well developed); caudal fin deeply forked, with pointed lobes (vs. caudal-fin frequently truncate, emarginate, or lunate).
Lethrinidae
Emperors

Lethrinidae differ in having a preopercular margin usually smooth (vs. usually serrate); branchiostegal rays 6 (vs. 7); dorsal-fin soft rays 9 or 10 (vs. usually 11 or more); no teeth on vomer (vs. teeth usually present); cheek scales lacking (vs. present) and lips frequently fleshy (vs. usually not fleshy).
Nemipteridae
Threadfin bream
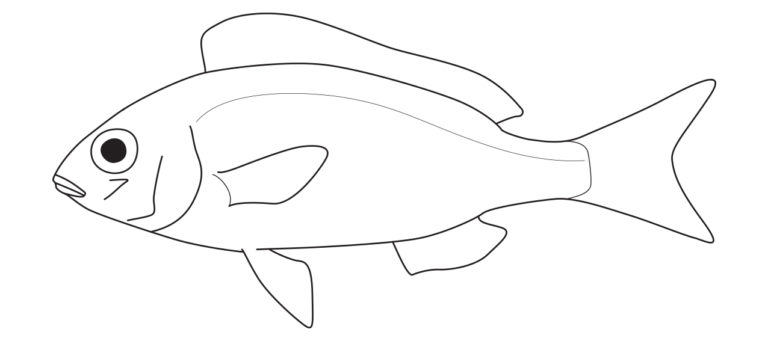
Nemipteridae differ in having a preopercular margin usually smooth (vs. usually serrate); dorsal-fin soft rays 9 (vs. usually 10 or more); anal-fin soft rays usually 7, rarely 8 (vs. usually 8 or more); branchiostegal rays 6 (vs. 7) and no teeth on vomer or palatines (vs. teeth present).
Sparidae
Sea bream
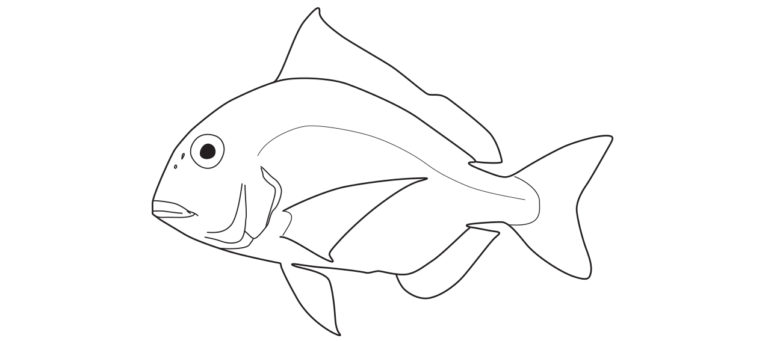
Sparidae differ in having a preopercular margin usually smooth (vs. usually serrate); branchiostegal rays 6 (vs. 7) and teeth in jaws variable - conical, incisiform, or molariform (vs. no incisiform teeth).
Haemulidae
Grunts, sweetlips
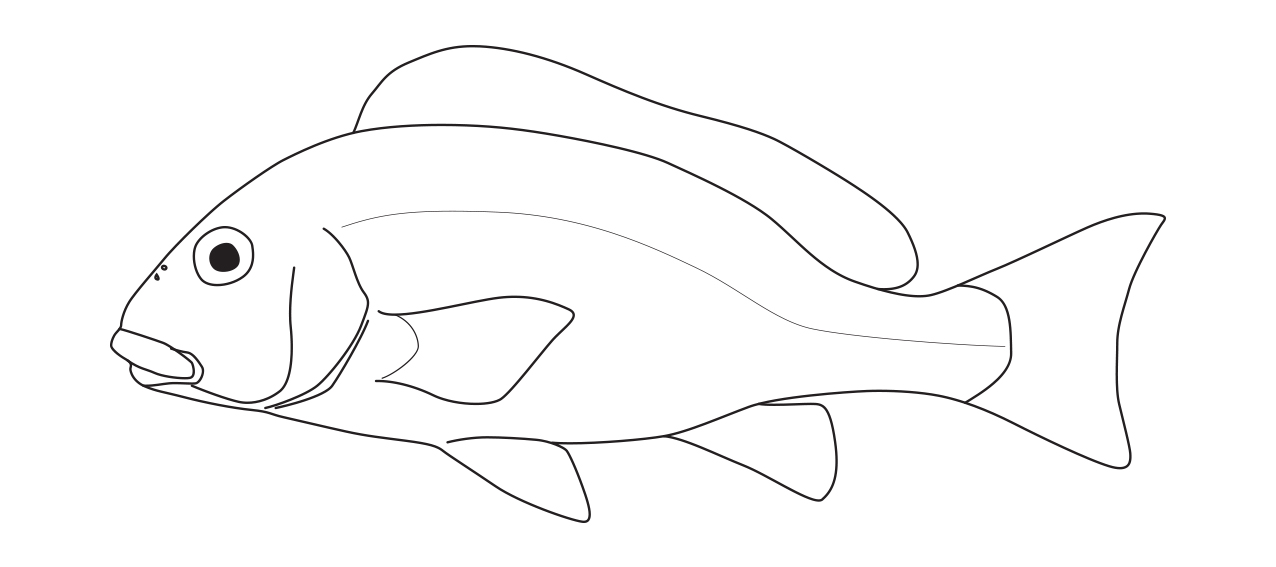
Haemulidae differ in having pores on chin (vs. pores absent); teeth conical, no canines (vs. canine teeth usually present) and second anal-fin spine very strong (vs. weak).
- Anderson, W.D. and Allen, G.R. Lutjanidae in: Carpenter, K, Niem, V. FAO species identification guide for fishery purposes. The living marine resources of the Western Central Pacific. Volume 5. Bony fishes part 3 (Menidae to Pomacentridae).. Rome: FAO; 2001; Volume 5; 2791-3380.



























































