Blue-grey above, silvery white below; opercular spot dusky; tongue greyish brown. Caudal, soft dorsal and anal fins greenish yellow to dusky.
Up to 28 cm TL.
Indo-West Pacific in tropical waters.
Adults found on coral and rocky reefs, from 20 to 140 m depth. Juveniles from in shallow sandy bays. Can also tolerate turbid waters.
Feeds on crustaceans, small squids and fishes.
Caught mainly by hook-and-line, bottom trawls, gill nets and traps.
Atropus armatus
Longfin trevally
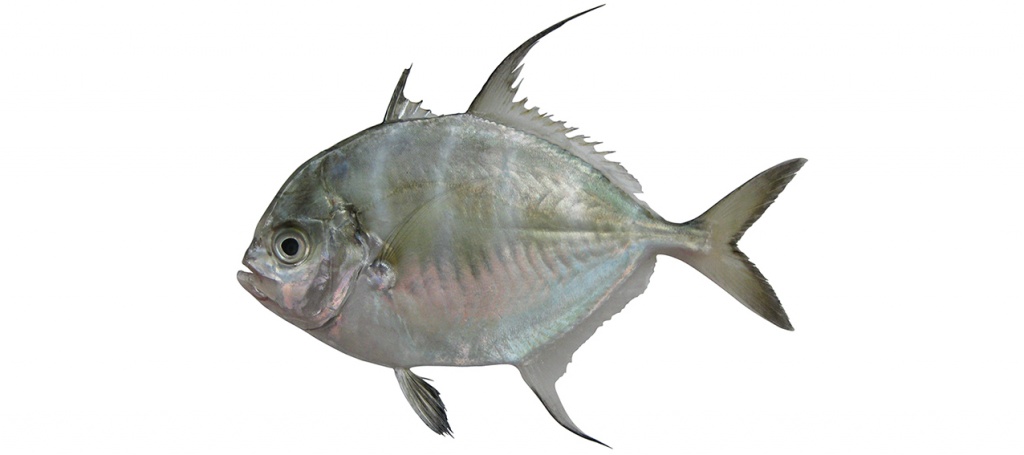

Atropus armatus differs in having the second dorsal-fin lobe long, greater than head length (vs. short, less than head length); second dorsal-fin central rays filamentous in males >21 cm FL (vs. never filamentous); scaleless breast area short ventrally, extending to pectoral-fin base (vs. long ventrally, extending to second anal-fin origin) and scaleless breast area small, extending to pectoral-fin base only (vs. large, covering area above and in front of pectoral-fin base).
Platycaranx chrysophrys
Longnose trevally
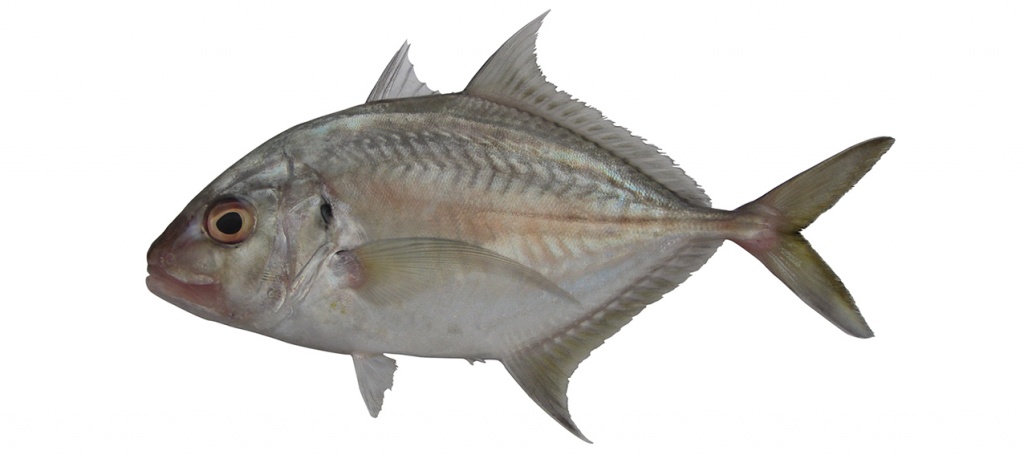

Platycaranx chrysophrys differs in having the head profile just above mouth vertical (vs. gently sloping); scaleless breast area short ventrally, often extending to behind pelvic fins (vs. long ventrally, extending to second anal-fin origin) and gill rakers (including rudiments) on first gill arch 21–26 (vs. 32–38).
Turrum coeruleopinnatus
Coastal trevally
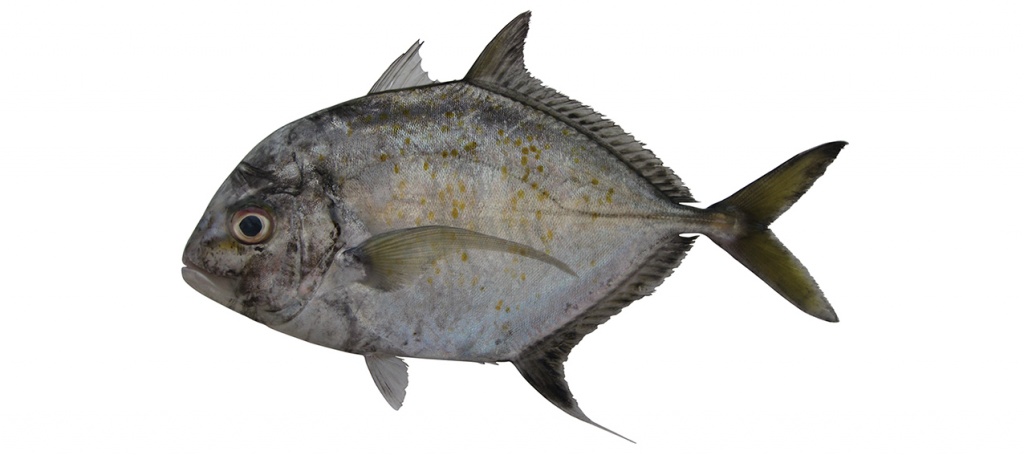

Turrum coeruleopinnatus differ in having scaleless breast area short ventrally, often extending to pectoral-fin base (vs. long ventrally, extending to second anal-fin origin); scaleless breast area small, extending to pectoral-fin base only (vs. large, covering area above and in front of pectoral-fin base) and gill rakers (including rudiments) on first gill arch 21–27 (vs. 32–38).
Carangichthys dinema
Shadow trevally
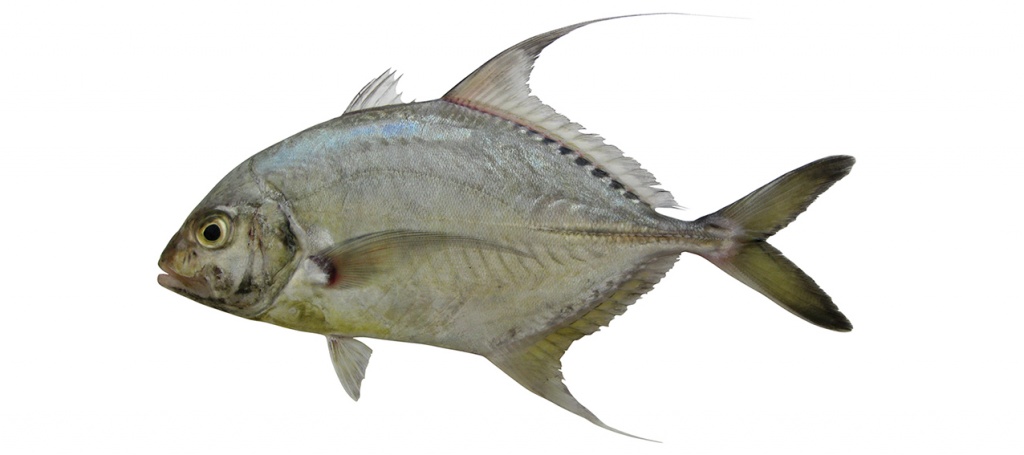

Carangichthys dinema differs in having brown blotches between bases of second dorsal-fin rays (vs. no markings); straight part of lateral line slightly shorter than curved part (vs. much shorter) and scaleless breast area short ventrally, extending to pelvic-fin origin (vs. long ventrally, often extending to second anal-fin origin).
Atropus hedlandensis
Bumpnose trevally
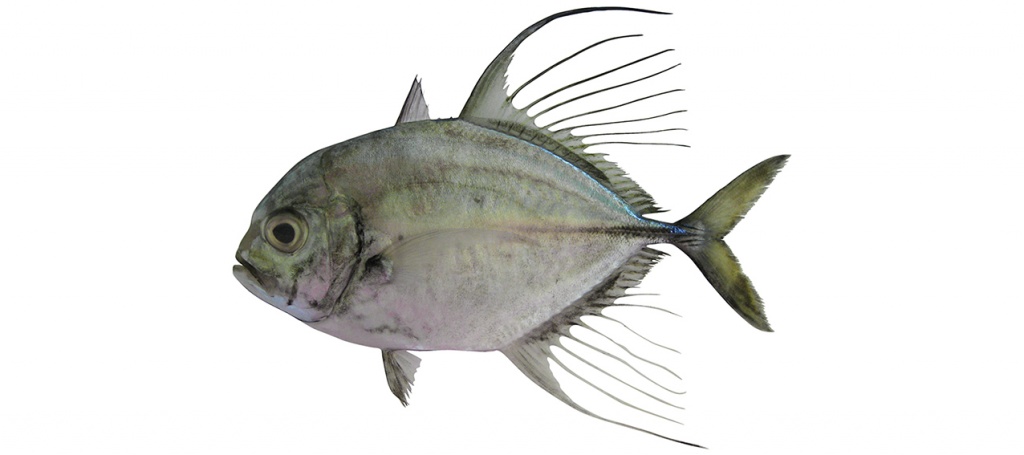
Atropus hedlandensis differs in having a second dorsal-fin lobe short, less than head length (vs. long, greater than head length); second dorsal-fin central rays long and filamentous in males >16.5 cm FL (vs. never filamentous); scaleless breast area shorter ventrally, often extending to pelvic-fin origin (vs. long ventrally, extending to second anal-fin origin) and scaleless breast area large, extending to area above and in front of pectoral-fin base (vs. small, extending to pectoral-fin base only).
Carangichthys oblongus
Coachwhip trevally
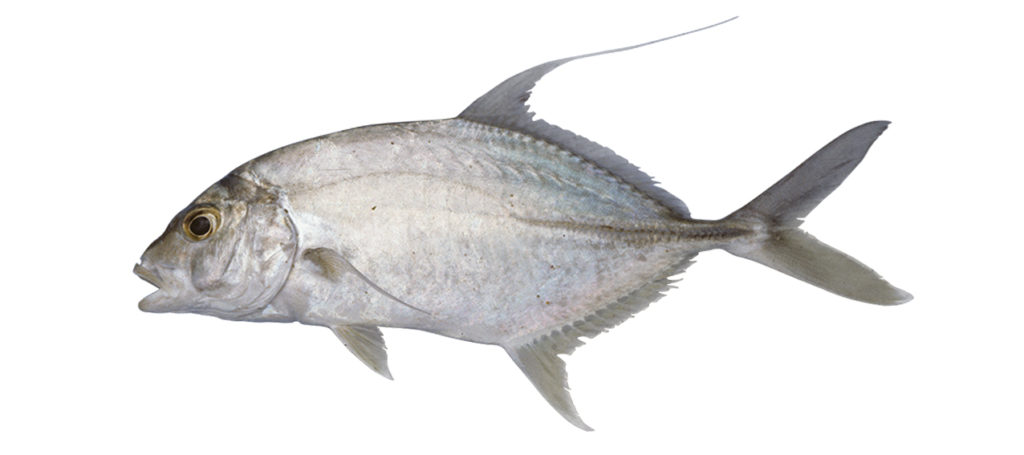

Carangichthys oblongus differs in having second dorsal-fin lobe longer than head (vs. shorter than head) and blue/black blotches between bases of second dorsal-fin rays (vs. no markings).
Platycaranx talamparoides
Imposter trevally
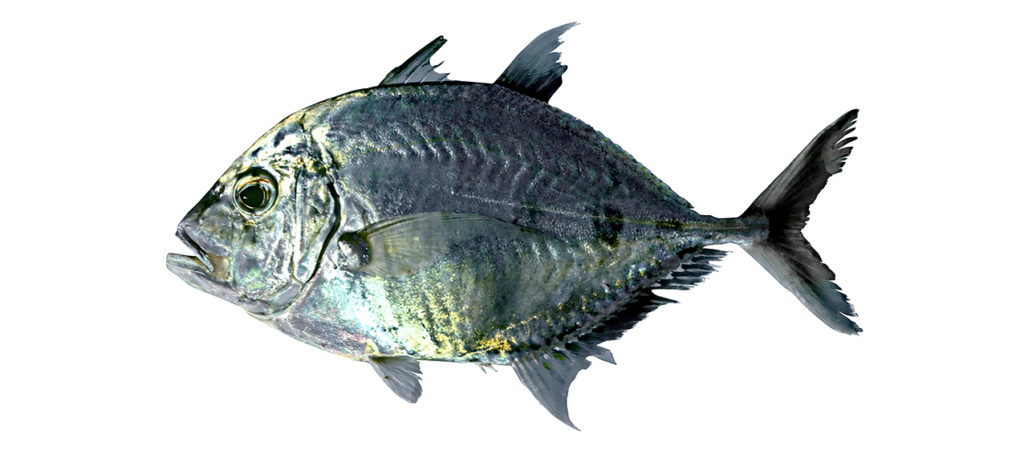

Platycaranx talamparoides differs in having the tongue white to pale grey (vs. greyish brown to brown) and gill rakers (including rudiments) on first gill arch 27–31 (vs. 32–38).
-
Osteichthyes
Bony Fish
-
-
Carangidae
Trevallies, queenfish, scads etc.
-
- Genus Alectis
- Genus Alepes
- Genus Gnathanodon
- Genus Megalaspis
- Genus Naucrates
- Genus Parastromateus
- Genus Selaroides
- Genus Seriolina
- Genus Atule
- Genus Elagatis
- Genus Carangoides
- Genus Decapterus
- Genus Caranx
- Genus Scomberoides
- Genus Selar
- Genus Seriola
- Genus Trachinotus
- Genus Ulua
-
- Genus Uraspis
-
Atropus atropos
Cleftbelly trevally
-
Serranidae
Groupers
-
- Genus Aethaloperca
-
- Genus Cephalopholis
-
-
Cephalopholis aitha
Rusty hind
-
Cephalopholis sonnerati
Tomato grouper
-
Cephalopholis argus
Peacock grouper
-
Cephalopholis cyanostigma
Bluespotted grouper
-
Cephalopholis miniata
Red coral grouper
-
Cephalopholis sexmaculata
Saddle grouper
-
Cephalopholis aurantia
Golden grouper
-
Cephalopholis boenak
Chocolate grouper
-
Cephalopholis microprion
Freckled grouper
-
Cephalopholis formosa
Bluelined grouper
-
Cephalopholis polleni
Harlequin grouper
-
Cephalopholis urodeta
Darkfin grouper
-
Cephalopholis spiloparaea
Strawberry grouper
-
Cephalopholis leopardus
Leopard grouper
-
Cephalopholis igarashiensis
Garish grouper
-
Cephalopholis aitha
- Genus Anyperodon
- Genus Caprodon
- Genus Chromileptes
- Genus Epinephelus
-
-
Epinephelus bontoides
Palemargin grouper
-
Epinephelus kupangensis
Kupang grouper
-
Epinephelus multinotatus
White-blotched grouper
-
Epinephelus morrhua
Comet grouper
-
Epinephelus quoyanus
Longfin grouper
-
Epinephelus spilotoceps
Foursaddle grouper
-
Epinephelus erythrurus
Cloudy grouper
-
Epinephelus polystigma
White-dotted grouper
-
Epinephelus amblycephalus
Banded grouper
-
Epinephelus sexfasciatus
Sixbar grouper
-
Epinephelus areolatus
Areolate grouper
-
Epinephelus bleekeri
Bleeker’s grouper
-
Epinephelus coeruleopunctatus
Whitespotted grouper
-
Epinephelus coioides
Orangespotted grouper
-
Epinephelus corallicola
Coral grouper
-
Epinephelus cyanopodus
Speckled grouper
-
Epinephelus undulosus
Wavylined grouper
-
Epinephelus epistictus
Dotted grouper
-
Epinephelus fasciatus
Blacktip grouper
-
Epinephelus flavocaeruleus
Blue and yellow grouper
-
Epinephelus heniochus
Brindle grouper
-
Epinephelus lanceolatus
Giant grouper
-
Epinephelus miliaris
Netfin grouper
-
Epinephelus retouti
Redtipped grouper
-
Epinephelus stictus
Blackdotted grouper
-
Epinephelus fuscoguttatus
Brownmarbled grouper
-
Epinephelus latifasciatus
Striped grouper
-
Epinephelus longispinis
Longspine grouper
-
Epinephelus maculatus
Highfin grouper
-
Epinephelus magniscuttis
Spotted grouper
-
Epinephelus malabaricus
Malabar grouper
-
Epinephelus ongus
Whitestreaked grouper
-
Epinephelus poecilonotus
Dotdash grouper
-
Epinephelus polyphekadion
Camouflage grouper
-
Epinephelus radiatus
Obliquebanded grouper
-
Epinephelus rivulatus
Halfmoon grouper
-
Epinephelus faveatus
Indian grouper
-
Epinephelus hexagonatus
Starspotted grouper
-
Epinephelus macrospilos
Snubnose grouper
-
Epinephelus melanostigma
Blackspot grouper
-
Epinephelus bontoides
- Genus Giganthias
- Genus Gracila
- Genus Liopropoma
-
-
Liopropoma swalesi
Swales' basslet
-
Liopropoma randalli
Indian basslet
-
Liopropoma multilineatum
Manyline perch
-
Liopropoma dorsoluteum
Yellowback basslet
-
Liopropoma collettei
Collette's basslet
-
Liopropoma lemniscatum
Ribbon basslet
-
Liopropoma mitratum
Pinstripe basslet
-
Liopropoma africanum
African basslet
-
Liopropoma susumi
Meteor perch
-
Liopropoma swalesi
- Genus Odontanthias
- Genus Plectranthias
- Genus Chelidoperca
-
- Genus Diploprion
-
Genus Variola
Lyretail
- Genus Plectropomus
- Genus Hyporthodus
-
Pseudanthias squamipinnis
Scalefin anthias
-
Sacura parva
Little fairy basslet
-
Selenanthias analis
Pearlspot fairy basslet
-
Epinephelus merra
Honeycomb grouper
-
Aethaloperca rogaa
Redmouth grouper
-
Stromateidae
Pomfrets
-
Coryphaenidae
Dolphinfishes
-
Balistidae
Triggerfishes
-
Haemulidae
Grunts, sweetlips
-
- Genus Diagramma
- Genus Plectorhinchus
-
-
Plectorhinchus albovittatus
Giant sweetlips
-
Plectorhinchus chaetodonoides
Harlequin sweetlips
-
Plectorhinchus chrysotaenia
Goldlined sweetlips
-
Plectorhinchus flavomaculatus
Yellowspotted sweetlips
-
Plectorhinchus gibbosus
Humpback sweetlips
-
Plectorhinchus lessonii
Striped sweetlips
-
Plectorhinchus lineatus
Lined sweetlips
-
Plectorhinchus polytaenia
Ribbon sweetlips
-
Plectorhinchus unicolor
Sombre Sweetlips
-
Plectorhinchus vittatus
Oriental sweetlips
-
Plectorhinchus pica
Painted sweetlip
-
Plectorhinchus albovittatus
- Genus Pomadasys
-
Monacanthidae
Leatherjackets
-
Lutjanidae
Snappers
-
- Genus Aphareus
- Genus Etelis
-
Genus Lutjanus
Snapper
-
-
Lutjanus dodecacanthoides
Sunbeam snapper
-
Lutjanus argentimaculatus
Mangrove jack
-
Lutjanus bengalensis
Bengal snapper
-
Lutjanus biguttatus
Twospot snapper
-
Lutjanus bitaeniatus
Indonesian snapper
-
Lutjanus bohar
Red bass
-
Lutjanus boutton
Button snapper
-
Lutjanus carponotatus
Spanish flag
-
Lutjanus decussatus
Chequered snapper
-
Lutjanus ehrenbergii
Ehrenberg's snapper
-
Lutjanus erythropterus
Crimson snapper
-
Lutjanus fulviflamma
Blackspot snapper
-
Lutjanus fulvus
Blacktail snapper
-
Lutjanus gibbus
Paddletail snapper
-
Lutjanus johnii
Golden snapper
-
Lutjanus kasmira
Common bluestripe snapper
-
Lutjanus lemniscatus
Darktail snapper
-
Lutjanus lunulatus
Lunartail snapper
-
Lutjanus lutjanus
Bigeye snapper
-
Lutjanus malabaricus
Malabar snapper
-
Lutjanus maxweberi
Pygmy snapper
-
Lutjanus mizenkoi
Mizenko's snapper
-
Lutjanus monostigma
Onespot snapper
-
Lutjanus papuensis
Papuan snapper
-
Lutjanus quinquelineatus
Fivelined snapper
-
Lutjanus rivulatus
Speckled snapper
-
Lutjanus rufolineatus
Goldenlined snapper
-
Lutjanus russellii
Russell's snapper
-
Lutjanus sebae
Red emperor
-
Lutjanus semicinctus
Black-banded snapper
-
Lutjanus timoriensis
Timor snapper
-
Lutjanus vitta
Brownstripe snapper
-
Lutjanus xanthopinnis
Yellowfin snapper
-
Lutjanus dodecacanthoides
- Genus Pristipomoides
-
-
Pristipomoides argyrogrammicus
Ornate jobfish
-
Pristipomoides auricilla
Goldflag jobfish
-
Pristipomoides filamentosus
Crimson jobfish
-
Pristipomoides flavipinnis
Goldeneye jobfish
-
Pristipomoides multidens
Goldband jobfish
-
Pristipomoides sieboldii
Lavender jobfish
-
Pristipomoides typus
Sharptooth jobfish
-
Pristipomoides zonatus
Oblique-banded snapper
-
Pristipomoides argyrogrammicus
- Genus Macolor
- Genus Paracaesio
- Genus Pinjalo
-
Lipocheilus carnolabrum
Tang's snapper
-
Symphorichthys spilurus
Sailfin snapper
-
Symphorus nematophorus
Chinamanfish
-
Aprion virescens
Green jobfish
-
Gempylidae
Snake mackerels
-
- Genus Rexea
-
Diplospinus multistriatus
Striped escolar
-
Nealotus tripes
Black snake mackerel
-
Neoepinnula orientalis
Sackfish
-
Nesiarchus nasutus
Black gemfish
-
Gempylus serpens
Snake mackerel
-
Lepidocybium flavobrunneum
Escolar
-
Promethichthys prometheus
Singleline Gemfish
-
Ruvettus pretiosus
Oilfish
-
Thyrsitoides marleyi
Black Snoek
-
Istiophoridae
Billfishes
-
Scombridae
Tunas & Mackerels
-
-
Genus Auxis
Frigate & bullet tunas
-
Genus Rastrelliger
Chub mackerel
-
Genus Scomberomorus
Mackerel
-
Genus Thunnus
True tunas
-
Acanthocybium solandri
Wahoo
-
Euthynnus affinis
Mackerel tuna
-
Grammatorcynus bilineatus
Double-lined mackerel
-
Gymnosarda unicolor
Dogtooth tuna
-
Katsuwonus pelamis
Skipjack tuna
-
Sarda orientalis
Striped bonito
-
Scomber australasicus
Blue mackerel
-
Genus Auxis
-
Xiphiidae
Broadbill swordfish
-
Sphyraenidae
Barracudas
-
Lethrinidae
Emperors
-
- Genus Gymnocranius
-
-
Gymnocranius elongatus
Forktail large-eye bream
-
Gymnocranius frenatus
Yellowsnout large-eye bream
-
Gymnocranius grandoculis
Blue-lined large-eye bream
-
Gymnocranius microdon
Bluespotted large-eye bream
-
Gymnocranius euanus
Japanese large-eye bream
-
Gymnocranius griseus
Grey large-eye bream
-
Gymnocranius satoi
Blacknape large-eye bream
-
Gymnocranius obesus
Obese large-eye bream
-
Gymnocranius elongatus
-
Genus Lethrinus
Emperor
-
-
Lethrinus atkinsoni
Yellowtail emperor
-
Lethrinus erythracanthus
Yellowfin emperor
-
Lethrinus erythropterus
Longfin emperor
-
Lethrinus genivittatus
Longspine emperor
-
Lethrinus harak
Thumbprint emperor
-
Lethrinus lentjan
Pinkear emperor
-
Lethrinus microdon
Smalltooth Emperor
-
Lethrinus nebulosus
Spangled emperor
-
Lethrinus obsoletus
Orangestriped Emperor
-
Lethrinus olivaceus
Longface emperor
-
Lethrinus ornatus
Ornate emperor
-
Lethrinus rubrioperculatus
Spotcheek emperor
-
Lethrinus semicinctus
Blackblotch emperor
-
Lethrinus variegatus
Slender emperor
-
Lethrinus xanthochilus
Yellowtip emperor
-
Lethrinus ravus
Drab emperor
-
Lethrinus reticulatus
Red snout emperor
-
Lethrinus conchyliatus
Maldive emperor
-
Lethrinus laticaudis
Grass emperor
-
Lethrinus miniatus
Trumpet emperor
-
Lethrinus atkinsoni
- Genus Monotaxis
-
Gnathodentex aureolineatus
Striped Large-eye Bream
-
Lethrinus amboinensis
Ambon emperor
-
Wattsia mossambica
Mozambique large-eye bream
-
Carangidae
-
Elasmobranchii
Cartilaginous Fish
-
-
Stegostomatidae
Zebra shark
-
-
Galeocerdidae
Tiger shark
-
Mobulidae
Manta and devil rays
-
Alopiidae
Thresher sharks
-
Lamnidae
Mackerel sharks
-
Carcharhinidae
Whaler sharks
-
- Genus Carcharhinus
-
-
Carcharhinus albimarginatus
Silvertip shark
-
Carcharhinus altimus
Bignose shark
-
Carcharhinus amblyrhynchoides
Graceful shark
-
Carcharhinus amblyrhynchos
Grey reef shark
-
Carcharhinus amboinensis
Pigeye shark
-
Carcharhinus borneensis
Borneo shark
-
Carcharhinus brevipinna
Spinner shark
-
Carcharhinus falciformis
Silky shark
-
Carcharhinus leucas
Bullshark
-
Carcharhinus limbatus
Common blacktip shark
-
Carcharhinus longimanus
Oceanic whitetip shark
-
Carcharhinus macloti
Hardnose shark
-
Carcharhinus melanopterus
Blacktip reef shark
-
Carcharhinus obscurus
Dusky shark
-
Carcharhinus plumbeus
Sandbar shark
-
Carcharhinus sealei
Blackspot shark
-
Carcharhinus sorrah
Spot-tail shark
-
Carcharhinus tilstoni
Australian blacktip shark
-
Carcharhinus tjutjot
Indonesian whaler shark
-
Carcharhinus albimarginatus
- Genus Rhizoprionodon
-
Glyphis gangeticus
Ganges shark
-
Lamiopsis tephrodes
Borneo broadfin shark
-
Loxodon macrorhinus
Sliteye shark
-
Negaprion acutidens
Sicklefin lemon shark
-
Prionace glauca
Blue shark
-
Scoliodon macrorhynchos
Pacific spadenose shark
-
Triaenodon obesus
Whitetip reef shark
-
Stegostomatidae
-
Crustaceans
Crabs, Lobsters, Shrimps, etc.